Styrofoam Recycling Machine
Reclaim your space. Reduce your volume. Recycle your foam.
EPS foam, Styrofoam packaging, EPE cushioning, and XPS insulation boards are widely used in packaging, construction, and logistics — but they’re also a major source of volume-heavy, non-biodegradable waste. At our recycling station, we help businesses, manufacturers, and municipalities turn waste polystyrene foam into recyclable material using advanced foam compactors, melting machines, pelletizing machines, shredding systems and other styrofoam recycling machines.
Why Foam Recycling Matters?
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), Styrofoam, and EPE foam are among the most common yet challenging plastic wastes in the world. Lightweight yet bulky, these materials consume significant storage space and are notoriously slow to decompose in landfills. Worse, loose foam particles pollute waterways and urban environments, posing a threat to marine life and municipal systems.
Proper foam recycling reduces plastic pollution, lowers transportation costs, and creates valuable raw material for secondary use in plastic pelletizing or construction. Whether you’re running a recycling station, warehouse, packaging plant, or logistics center—foam waste is both a challenge and an opportunity.
How to Recycle Foam Waste?
Collection & Sorting of Foam Waste
We begin by collecting foam materials from various sources, such as packaging warehouses, construction sites, supermarkets, and logistics centers. Upon arrival, the foam is manually or automatically sorted by type and cleanliness:
- EPS (Expanded Polystyrene): typically used for electronics packaging and insulation boards.
- EPE (Expanded Polyethylene): found in cushioning sheets and fruit trays.
- XPS (Extruded Polystyrene): rigid foam used in construction.
- Contaminated or food-grade foam: such as takeout containers.
Sorting helps determine the best processing method—cold press, hot melting, or shredding—for each batch, ensuring efficient recycling and material purity.
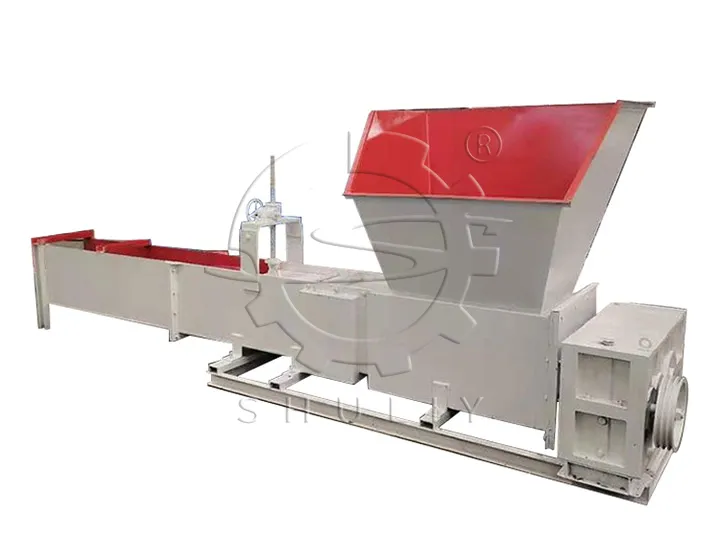
Cold Press Compaction
For clean and dry EPS foam, we use cold press foam compactors—either vertical or horizontal—to reduce volume by up to 30–50 times. This styrofoam recycling machine uses a powerful screw compression system to crush and compress the foam into dense blocks without heat. Cold pressing is energy-efficient, quiet, and environmentally friendly, making it ideal for urban areas or small recycling stations. The resulting compressed foam blocks are stackable, lightweight, and ready for transport or resale.
Hot Melting & Extrusion
When dealing with contaminated foam, such as food-grade trays, meat containers, or wet materials, we use EPS hot melting machines. These machines heat the foam to a specific temperature, melt it, and extrude it through a screw into a continuous log. This process achieves a higher compression ratio (up to 90:1) than cold pressing and stabilizes the material for long-term storage or pelletizing. Melted foam logs are easy to stack, export, or feed into plastic pelletizing lines.
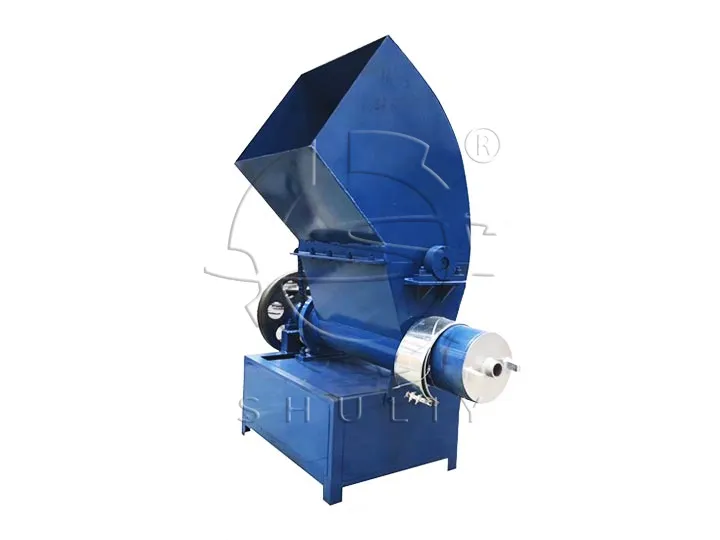
Shredding of Large or Flexible Foam
EPE rolls, oversized foam blocks, and flexible packaging foams require pre-shredding before melting or compacting. We use foam shredders to reduce large items into uniform, manageable flakes. This step improves the efficiency and throughput of downstream equipment such as hot melters or horizontal compactors. Shredded foam also ensures more consistent melting and reduces machine jamming.
Packing, Storage & Secondary Processing (Pelletizing)
The final step is packing the output—either in the form of compressed blocks or melted logs—into bales or containers for storage, sale, or export. Depending on the customer’s different needs:
- Stack foam blocks on pallets and wrap for shipment
- Feed melted logs directly into EPS pelletizing machines
- Bundle shredded flakes for reprocessing
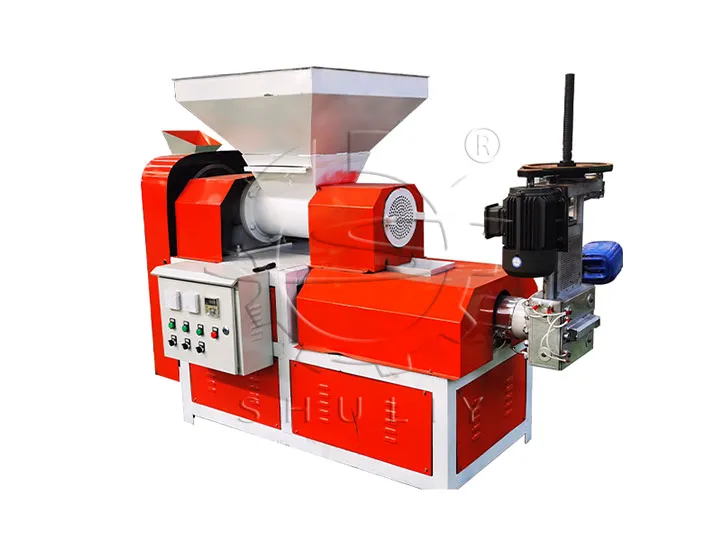
Turning Compressed Foam into Recycled Plastic Pellets
Once the foam has been shredded, compacted or melted, it can be further processed into reusable plastic through EPS pelletizing. We feed the compressed blocks or melted foam logs into a foam granulation machine, where the material is heated, plasticized, filtered, and finally cut into uniform EPS pellets using a strand or water-ring cutting system. These recycled granules can be reused in injection molding, extruded sheets, plastic boards, or even new foam products—giving waste foam a valuable second life.
Types of Foam Our Styrofoam Recycling Machine Process
At our styrofoam recycling machine facility, your recycling plants handle a wide range of plastic foam materials commonly found in packaging, construction, food service, and manufacturing industries. Below are the main types of foam we recycle, along with typical sources and examples of raw materials our clients often process.
EPS is one of the most commonly used foam materials. It’s lightweight, rigid, and widely used in protective packaging and insulation.
Common sources:
- TV, refrigerator, air-conditioner packaging
- Fragile item cushioning for electronics and appliances
- Construction insulation boards and sandwich panels
- Protective corners and foam blocks in shipping boxes
- Discarded EPS foam slabs from renovation sites
EPE is a soft, flexible, and shock-absorbing foam used widely in custom wrapping and logistics.
Common sources:
- Foam sheets and rolls used to wrap furniture or glass
- Fruit and vegetable trays (especially apple foam nets)
- Lining for express parcel packaging
- Yoga mats and sports protective gear packaging
- Soft foam buffers for electronics and household goods
XPS foam is known for its high strength and closed-cell structure, mostly used in insulation applications.
Common sources:
- Rigid wall insulation panels and thermal boards
- Underfloor heating foam sheets
- Sandwich board cores for prefab buildings
- Blue or green foam scraps from building sites
- Surplus XPS panels from construction material suppliers
Disposable foam containers made of EPS are lightweight and widely used in the food service industry.
Common sources:
- Used takeout boxes, lunch containers, and food trays
- Meat and seafood foam packaging from supermarkets
- Disposable cups and clamshell containers from restaurants
- Bakery and cake base boards
- Fast food chain foam trays (clean & dry only)